Page 10 - June-2022
P. 10
TECHNICAL PAPER
specimens. Nevertheless, the larger difference between the transverse reinforcement is to control the width of the diagonal
design and observed shear strengths indicates the conservative shear crack. The current ACI 318-19 code does not provide
[3]
approach adopted in the design codes to avoid the shear failure specific guidelines for the limiting size of shear and flexural
of concrete beams in practice. cracks. However, ACI 224R-01 [14] guidelines suggest that the
maximum allowable crack width should not exceed 0.41 mm
4.2 Ultimate strength under the service load condition. A more stringent limit of 0.3
mm is recommended in IS: 456 (2000) provisions. The service
[2]
Table 2 summarizes the design shear strengths computed load is taken as 60 % of the nominal shear strength capacity
using ACI 318-19 and IS: 456 (2000) provisions for all test of the beam section as per ACI 224R-01 [14] guidelines. Table 2
[2]
[3]
specimens. All test specimens exhibited significant overstrength shows the values of shear strengths of beams at the service load
in the range of 3.5-3.6 as compared to the design shear
strengths. Even though all beams were designed to fail in levels. The width of diagonal shear cracks in specimens was
shear, the specimens with the high-strength concrete (M50) and measured at different load levels during the experiment.
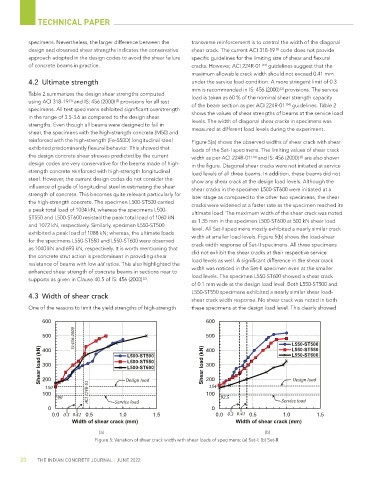
reinforced with the high-strength (Fe-550D) longitudinal steel Figure 5(a) shows the observed widths of shear crack with shear
exhibited predominantly flexural behavior. This showed that loads of the Set-I specimens. The limiting values of shear crack
the design concrete shear stresses predicted by the current width as per ACI 224R-01 [14] and IS: 456 (2000) are also shown
[2]
design codes are very conservative for the beams made of high- in the figure. Diagonal shear cracks were not initiated at service
strength concrete reinforced with high-strength longitudinal load levels of all three beams. In addition, these beams did not
steel. However, the current design codes do not consider the show any shear crack at the design load levels. Although the
influence of grade of longitudinal steel in estimating the shear shear cracks in the specimen L500-ST600 were initiated at a
strength of concrete. This becomes quite relevant particularly for later stage as compared to the other two specimens, the shear
the high-strength concrete. The specimen L500-ST500 carried cracks were widened at a faster rate as the specimen reached its
a peak total load of 1034 kN, whereas the specimens L500- ultimate load. The maximum width of the shear crack was noted
ST550 and L500-ST600 resisted the peak total load of 1060 kN as 1.35 mm in the specimen L500-ST600 at 500 kN shear load
and 1072 kN, respectively. Similarly, specimen L550-ST500 level. All Set-I specimens mostly exhibited a nearly similar crack
exhibited a peak load of 1088 kN; whereas, the ultimate loads width at smaller load levels. Figure 5(b) shows the load-shear
for the specimens L550-ST550 and L550-ST600 were observed
as 1040 kN and 693 kN, respectively. It is worth mentioning that crack width response of Set-II specimens. All three specimens
the concrete strut action is predominant in providing shear did not exhibit the shear cracks at their respective service
resistance of beams with low a/d ratios. This also highlighted the load levels as well. A significant difference in the shear crack
enhanced shear strength of concrete beams in sections near to width was noticed in the Set-II specimen even at the smaller
supports as given in Clause 40.5 of IS: 456 (2000) . load levels. The specimen L550-ST600 showed a shear crack
[2]
of 0.1 mm wide at the design load level. Both L550-ST500 and
L550-ST550 specimens exhibited a nearly similar shear load-
4.3 Width of shear crack
shear crack width response. No shear crack was noted in both
One of the reasons to limit the yield strengths of high-strength these specimens at the design load level. This clearly showed
600 600
IS:456-2000 L550-ST500
500 500
400 400 L550-ST550
L500-ST500 L550-ST600
L500-ST550
300 L500-ST600 300
200 Design load 200 Design load
150 154
100 ACI 224R-01 100
90 Service load 92.5 Service load
0 0
0.0 0.3 0.41 0.5 1.0 1.5 0.0 0.3 0.41 0.5 1.0 1.5
Width of shear crack (mm) Width of shear crack (mm)
(a) (b)
Figure 5: Variation of shear crack width with shear loads of specimens: (a) Set-I; (b) Set-II
20 THE INDIAN CONCRETE JOURNAL | JUNE 2022