Page 8 - Open-Access-May-2020
P. 8
TECHNICAL PAPER
present in them during every casting operation. For the SCC
mixes, the quantity of material replaced by water was added and
the amount of water present in excess was reduced in the water-
cement ratio. This material compensation was necessary to get a
uniform mix of desired strength.
4.3 Reinforcing Steel
High yield strength deformed steel bars of Fe500 grade were
used as reinforcement in the inner and jacket regions (Table 2).
The yield strengths of reinforcements are based on 0.2%
proof stress. They were obtained from tension tests of coupon
specimens. The tension tests were conducted using a universal
testing machine.
(a) (b)
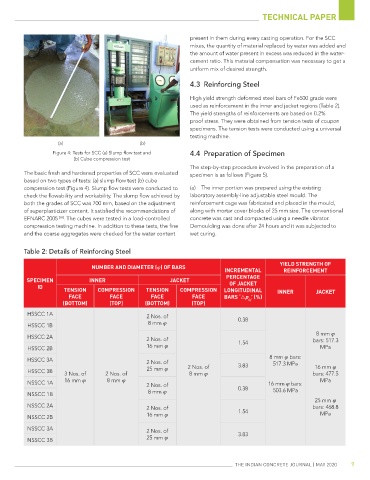
Figure 4: Tests for SCC (a) Slump flow test and 4.4 Preparation of Specimen
(b) Cube compression test
The step-by-step procedure involved in the preparation of a
The basic fresh and hardened properties of SCC were evaluated specimen is as follows (Figure 5).
based on two types of tests: (a) slump flow test (b) cube
compression test (Figure 4). Slump flow tests were conducted to (a) The inner portion was prepared using the existing
check the flowability and workability. The slump flow achieved by laboratory assembly-line adjustable steel mould. The
both the grades of SCC was 700 mm, based on the adjustment reinforcement cage was fabricated and placed in the mould,
of superplasticizer content. It satisfied the recommendations of along with mortar cover blocks of 25 mm size. The conventional
EFNARC 2005 [18] . The cubes were tested in a load-controlled concrete was cast and compacted using a needle vibrator.
compression testing machine. In addition to these tests, the fine Demoulding was done after 24 hours and it was subjected to
and the coarse aggregates were checked for the water content wet curing.
Table 2: Details of Reinforcing Steel
yielD StrengtH of
number anD Diameter (φ) of barS
incremental reinforcement
Percentage
SPecimen inner Jacket of Jacket
iD tenSion comPreSSion tenSion comPreSSion longituDinal
face face face face barS ‘△p ’ (%) inner Jacket
(bottom) (toP) (bottom) (toP) t,j
HSSCC 1A 2 Nos. of 0.38
HSSCC 1B 8 mm φ
8 mm φ
HSSCC 2A 2 Nos. of bars: 517.3
HSSCC 2B 16 mm φ 1.54 MPa
HSSCC 3A 2 Nos. of 8 mm φ bars:
517.3 MPa
16 mm φ
HSSCC 3B 3 Nos. of 2 Nos. of 25 mm φ 2 Nos. of 3.83 bars: 477.5
8 mm φ
NSSCC 1A 16 mm φ 8 mm φ 2 Nos. of 16 mm φ bars: MPa
8 mm φ 0.38 503.6 MPa
NSSCC 1B
25 mm φ
NSSCC 2A 2 Nos. of bars: 468.8
16 mm φ 1.54 MPa
NSSCC 2B
NSSCC 3A 2 Nos. of
25 mm φ 3.83
NSSCC 3B
The IndIan ConCreTe Journal | MaY 2020 9