Page 10 - Open-Access-June-2020
P. 10
TECHNICAL PAPER
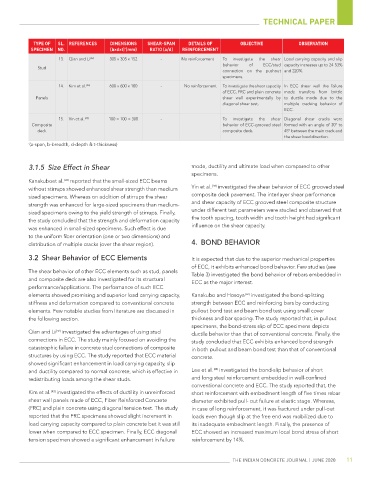
type of sl. referenCes dimensions shear-span details of oBjeCtive oBservation
speCimen no. (b×d×t) (mm) ratio (a/d) reinforCement
*
13. Qian and Li [42] 305 x 305 x 152 - No reinforcement To investigate the shear Load carrying capacity and slip
behavior of ECC/stud capacity increases up to 24-53%
Stud
connection on the pushout and 220%.
specimens.
14. Kim et al. [43] 600 x 600 x 100 - No reinforcement To investigate the shear capacity In ECC shear wall the failure
of ECC, FRC and plain concrete mode transfers from brittle
Panels shear wall experimentally by to ductile mode due to the
diagonal shear test. multiple cracking behavior of
ECC.
15. Yin et al. [44] 100 × 100 × 300 - To investigate the shear Diagonal shear cracks were
Composite behavior of ECC-grooved steel formed with an angle of 30° to
deck composite deck. 45° between the main crack and
the shear load direction.
* (a-span, b-breadth, d-depth & t-thickness)
3.1.5 Size Effect in shear mode, ductility and ultimate load when compared to other
specimens.
Kanakuboet al. reported that the small-sized ECC beams
[26]
[44]
without stirrups showed enhanced shear strength than medium Yin et al. investigated the shear behavior of ECC grooved steel
sized specimens. Whereas on addition of stirrups the shear composite deck pavement. The interlayer shear performance
strength was enhanced for large-sized specimens than medium- and shear capacity of ECC grooved steel composite structure
sized specimens owing to the yield strength of stirrups. Finally, under different test parameters were studied and observed that
the study concluded that the strength and deformation capacity the tooth spacing, tooth width and tooth height had significant
was enhanced in small-sized specimens. Such effect is due influence on the shear capacity.
to the uniform fiber orientation (one or two dimensions) and
distribution of multiple cracks (over the shear region). 4. BOND BEHAVIOR
3.2 Shear Behavior of ECC Elements It is expected that due to the superior mechanical properties
of ECC, it exhibits enhanced bond behavior. Few studies (see
The shear behavior of other ECC elements such as stud, panels Table 3) investigated the bond behavior of rebars embedded in
and composite deck are also investigated for its structural ECC as the major interest.
performance/applications. The performance of such ECC
elements showed promising and superior load carrying capacity, Kanakubo and Hosoya investigated the bond-splitting
[47]
stiffness and deformation compared to conventional concrete strength between ECC and reinforcing bars by conducting
elements. Few notable studies from literature are discussed in pullout bond test and beam bond test using small cover
the following section. thickness and bar spacing. The study reported that, in pullout
specimens, the bond-stress slip of ECC specimens depicts
Qian and Li investigated the advantages of using stud ductile behavior than that of conventional concrete. Finally, the
[42]
connections in ECC. The study mainly focused on avoiding the study concluded that ECC exhibits enhanced bond strength
catastrophic failure in concrete stud connections of composite in both pullout and beam bond test than that of conventional
structures by using ECC. The study reported that ECC material concrete.
showed significant enhancement in load carrying capacity, slip
[48]
and ductility compared to normal concrete, which is effective in Lee et al. investigated the bond-slip behavior of short
redistributing loads among the shear studs. and long steel reinforcement embedded in well-confined
conventional concrete and ECC. The study reported that, the
Kim et al. investigated the effects of ductility in unreinforced short reinforcement with embedment length of five times rebar
[43]
shear wall panels made of ECC, Fiber Reinforced Concrete diameter exhibited pull- out failure at elastic stage. Whereas,
(FRC) and plain concrete using diagonal tension test. The study in case of long reinforcement, it was fractured under pull-out
reported that the FRC specimens showed slight increment in loads even though slip at the free end was mobilized due to
load carrying capacity compared to plain concrete but it was still its inadequate embedment length. Finally, the presence of
lower when compared to ECC specimen. Finally, ECC diagonal ECC showed an increased maximum local bond stress of short
tension specimen showed a significant enhancement in failure reinforcement by 14%.
The IndIan ConCreTe Journal | June 2020 11