Page 9 - March-2022
P. 9
TECHNICAL PAPER
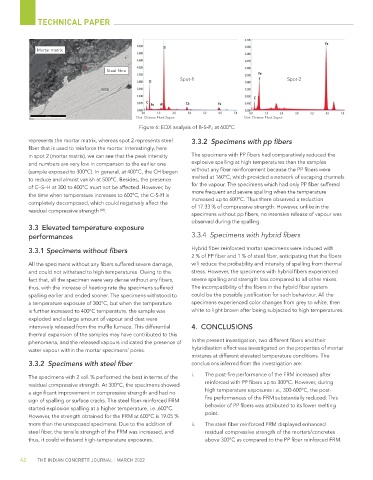
Mortar matrix
Steel fibre
Spot-1 Spot-2
Det: Octane Elect Super Det: Octane Elect Super
Figure 6: EDX analysis of B-S-P S at 600°C
represents the mortar matrix, whereas spot 2 represents steel 3.3.2 Specimens with pp fibers
fiber that is used to reinforce the mortar. Interestingly, here
in spot 2 (mortar matrix), we can see that the peak intensity The specimens with PP fibers had comparatively reduced the
and numbers are very low in comparison to the earlier one explosive spalling at high temperatures than the samples
(sample exposed to 300°C). In general, at 400°C, the CH began without any fiber reinforcement because the PP fibers were
to reduce and almost vanish at 500°C. Besides, the presence melted at 160°C, which provided a network of escaping channels
of C–S–H at 300 to 400°C must not be affected. However, by for the vapour. The specimens which had only PP fiber suffered
the time when temperature increases to 600°C, the C-S-H is more frequent and severe spalling when the temperature
increased up to 600°C. Thus there observed a reduction
completely decomposed, which could negatively affect the of 17.33 % of compressive strength. However, unlike in the
residual compressive strength [18] .
specimens without pp fibers, no intensive release of vapour was
observed during the spalling.
3.3 Elevated temperature exposure
performances 3.3.4 Specimens with hybrid fibers
3.3.1 Specimens without fibers Hybrid fiber reinforced mortar specimens were induced with
2 % of PP fiber and 1 % of steel fiber, anticipating that the fibers
All the specimens without any fibers suffered severe damage, will reduce the probability and intensity of spalling from thermal
and could not withstand to high temperatures. Owing to the stress. However, the specimens with hybrid fibers experienced
fact that, all the specimen were very dense without any fibers, severe spalling and strength loss compared to all other mixes.
thus, with the increase of heating rate the specimens suffered The incompatibility of the fibers in the hybrid fiber system
spalling earlier and ended sooner. The specimens withstood to could be the possible justification for such behaviour. All the
a temperature exposure of 300°C, but when the temperature specimens experienced color changes from grey to white, then
is further increased to 400°C temperature, the sample was white to light brown after being subjected to high temperatures.
exploded and a large amount of vapour and dust were
intensively released from the muffle furnace. This differential 4. CONCLUSIONS
thermal expansion of the samples may have contributed to this
phenomena, and the released vapours indicated the presence of In the present investigation, two different fibers and their
water vapour within the mortar specimens’ pores. hybridisation effect was investigated on the properties of mortar
mixtures at different elevated temperature conditions. The
3.3.2 Specimens with steel fiber conclusions inferred from the investigation are:
The specimens with 2 vol. % performed the best in terms of the i. The post-fire performance of the FRM increased after
residual compressive strength. At 300°C, the specimens showed reinforced with PP fibers up to 300°C. However, during
a significant improvement in compressive strength and had no high temperature exposures i.e., 300-600°C, the post-
sign of spalling or surface cracks. The steel fiber-reinforced FRM fire performances of the FRM substantially reduced. This
started explosion spalling at a higher temperature, i.e.,600°C. behavior of PP fibers was attributed to its lower melting
However, the strength obtained for the FRM at 600°C is 19.05 % point.
more than the unexposed specimens. Due to the addition of ii. The steel fiber reinforced FRM displayed enhanced
steel fiber, the tensile strength of the FRM was increased, and residual compressive strength of the mortars/concretes
thus, it could withstand high-temperature exposures. above 300°C as compared to the PP fiber reinforced FRM.
42 THE INDIAN CONCRETE JOURNAL | MARCH 2022