Page 8 - March-2022
P. 8
TECHNICAL PAPER
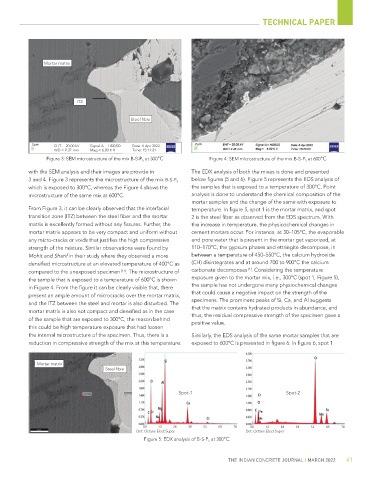
Mortar matrix
ITZ
Steel fibre
EHT = 20.00 kV Signal A = HDBSD Date: 6 Apr 2022
WD = 9.37 mm Mag = 6.00 K X Time: 15:11:31
Figure 3: SEM microstructure of the mix B-S-P S at 300°C Figure 4: SEM microstructure of the mix B-S-P S at 600°C
with the SEM analysis and their images are provide in The EDX analysis of both the mixes is done and presented
3 and 4. Figure 3 represents the microstructure of the mix B-S-P S below figures (5 and 6). Figure 5 represents the EDS analysis of
which is exposed to 300°C, whereas the Figure 4 shows the the samples that is exposed to a temperature of 300°C. Point
microstructure of the same mix at 600°C. analysis is done to understand the chemical composition of the
mortar samples and the change of the same with exposure to
From Figure 3, it can be clearly observed that the interfacial temperature. In figure 5, spot 1 is the mortar matrix, and spot
transition zone (ITZ) between the steel fiber and the mortar 2 is the steel fiber as observed from the EDS spectrum. With
matrix is excellently formed without any fissures. Further, the the increase in temperature, the physicochemical changes in
mortar matrix appears to be very compact and uniform without cement mortars occur. For instance, at 30–105°C, the evaporable
any micro-cracks or voids that justifies the high compressive and pore water that is present in the mortar get vaporized, at
strength of the mixture. Similar observations were found by 110–170°C, the gypsum phases and ettringite decompose, in
Mohit and Sharif in their study where they observed a more between a temperature of 450–550°C, the calcium hydroxide
densified microstructure at an elevated temperature of 400°C as (CH) disintegrates and at around 700 to 900°C the calcium
[1]
compared to the unexposed specimen [17] . The microstructure of carbonate decomposes . Considering the temperature
the sample that is exposed to a temperature of 600°C is shown exposure given to the mortar mix, i.e., 300°C (spot 1, Figure 5),
in Figure 4. From the figure it can be clearly visible that, there the sample has not undergone many physiochemical changes
present an ample amount of microcracks over the mortar matrix, that could cause a negative impact on the strength of the
and the ITZ between the steel and mortar is also disturbed. The specimens. The prominent peaks of Si, Ca, and Al suggests
mortar matrix is also not compact and densified as in the case that the matrix contains hydrated products in abundance, and
of the sample that are exposed to 300°C, the reason behind thus, the residual compressive strength of the specimen gave a
positive value.
this could be high temperature exposure that had loosen
the internal microstructure of the specimen. Thus, there is a Similarly, the EDS analysis of the same mortar samples that are
reduction in compressive strength of the mix at this temperature. exposed to 600°C is presented in figure 6. In figure 6, spot 1
Mortar matrix
Steel fibre
Spot-1 Spot-2
Det: Octane Elect Super Det: Octane Elect Super
Figure 5: EDX analysis of B-S-P S at 300°C
THE INDIAN CONCRETE JOURNAL | MARCH 2022 41