Page 7 - April-Month
P. 7
TECHNICAL PAPER
-550
3.0
-500
Severe
-450
2.5
-400 High
-350 2.0
HCP (mv) -300 Intermiddiate 2 1.5
-250
-200 i corr (mA/cm )
-150 1.0
-100
Low Risk 0.5
-50
0 0.0
C0 C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C0 C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8
Cycle Cycle
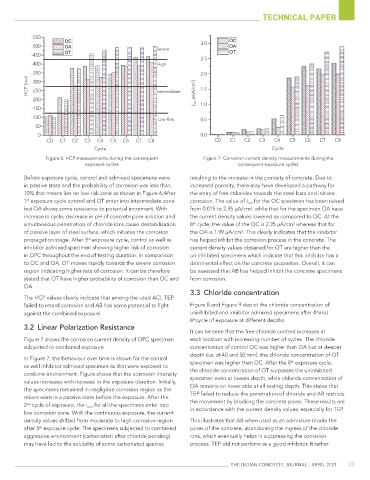
Figure 6: HCP measurements during the consequent Figure 7: Corrosion current density measurements during the
exposure cycles consequent exposure cycles
Before exposure cycle, control and admixed specimens were resulting to the increase in the porosity of concrete. Due to
in passive state and the probability of corrosion was less than increased porosity, there may have developed a pathway for
10% that means lies on low-risk zone as shown in Figure 6.After the entry of free chlorides towards the steel bars and initiate
1 exposure cycle control and OT enter into intermediate zone corrosion. The value of i corr for the OC specimen has been raised
st
but OA shows some resistance to potential increment. With from 0.015 to 2.35 µA/cm , while that for the specimen OA have
2
increase in cycle, decrease in pH of concrete pore solution and the current density values lowered as compared to OC. At the
th
simultaneous penetration of chloride ions cause destabilisation 8 cycle, the value of the OC is 2.35 µA/cm whereas that for
2
of passive layer of steel surface, which initiates the corrosion the OA is 1.99 µA/cm . This clearly indicates that the inhibitor
2
propagation stage. After 3 exposure cycle, control as well as has helped inhibit the corrosion process in the concrete. The
rd
inhibitor admixed specimen showing higher risk of corrosion current density values obtained for OT are higher than the
in OPC throughout the end of testing duration. In comparison un-inhibited specimens which indicate that this inhibitor has a
to OC and OA, OT moves rapidly towards the severe corrosion detrimental effect on the concrete properties. Overall, it can
region indicating higher rate of corrosion. It can be therefore be assessed that AB has helped inhibit the concrete specimens
stated that OT have higher probability of corrosion than OC and from corrosion.
OA.
3.3 Chloride concentration
The HCP values clearly indicate that among the used ACI, TEP
failed to retard corrosion and AB has some potential to fight Figure 8 and Figure 9 depict the chloride concentration of
th
against the combined exposure. uninhibited and inhibitor admixed specimens after 4 and
8 cycle of exposure at different depths.
th
3.2 Linear Polarization Resistance
It can be seen that the free chloride content increases at
Figure 7 shows the corrosion current density of OPC specimen each location with increasing number of cycles. The chloride
subjected to combined exposure. concentration of control OC was higher than OA but at deeper
depth (i.e. at 40 and 50 mm), the chloride concentration of OT
In Figure 7, the behaviour over time is shown for the control th
as well inhibitor admixed specimen as that were exposed to specimen was higher than OC. After the 8 exposure cycle,
combine environment. Figure shows that the corrosion intensity the chloride concentration of OT surpasses the uninhibited
values increases with increase in the exposure duration. Initially, specimen even at lowers depth, while chloride concentration of
the specimens remained in negligible corrosion region as the OA remains on lower side at all testing depth. This states that
rebars were in a passive state before the exposure. After the TEP failed to reduce the penetration of chloride and AB restricts
2 cycle of exposure, the i corr for all the specimens enter into the movement by blocking the concrete pores. These results are
nd
low corrosion zone. With the continuous exposure, the current in accordance with the current density values, especially for TEP.
density values shifted from moderate to high corrosion region This illustrates that AB when used as an admixture blocks the
after 5 exposure cycle. The specimens subjected to combined pores of the concrete, abandoning the ingress of the chloride
th
aggressive environment (carbonation after chloride ponding) ions, which eventually helps in suppressing the corrosion
may have led to the solubility of some carbonated species process. TEP did not perform as a good inhibitor. It rather
THE INDIAN CONCRETE JOURNAL | APRIL 2021 33