Page 4 - April-Month
P. 4
TECHNICAL PAPER
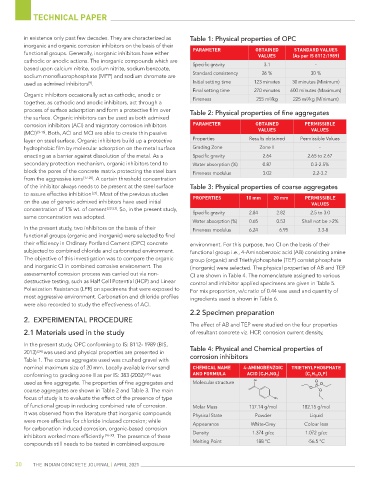
in existence only past few decades. They are characterized as Table 1: Physical properties of OPC
inorganic and organic corrosion inhibitors on the basis of their
STANDARD VALUES
functional groups. Generally, inorganic inhibitors have either PARAMETER OBTAINED (As per IS 8112:1989)
VALUES
cathodic or anodic actions. The inorganic compounds which are
Specific gravity 3.1 -
based upon calcium nitrite, sodium nitrite, sodium benzoate,
sodium monofluorophosphate (MFP) and sodium chromate are Standard consistency 26 % 30 %
used as admixed inhibitors . Initial setting time 123 minutes 30 minutes (Minimum)
[9]
Final setting time 270 minutes 600 minutes (Maximum)
Organic inhibitors occasionally act as cathodic, anodic or
Fineness 255 m /kg 225 m /kg (Minimum)
2
2
together, as cathodic and anodic inhibitors, act through a
process of surface adsorption and form a protective film over Table 2: Physical properties of fine aggregates
the surface. Organic inhibitors can be used as both admixed
corrosion inhibitors (ACI) and migratory corrosion inhibitors PARAMETER OBTAINED PERMISSIBLE
(MCI) [9-16] . Both, ACI and MCI are able to create thin passive VALUES VALUES
layer on steel surface. Organic inhibitors build up a protective Properties Results obtained Permissible Values
hydrophobic film by molecular adsorption on the metal surface Grading Zone Zone II -
enacting as a barrier against dissolution of the metal. As a Specific gravity 2.64 2.65 to 2.67
secondary protection mechanism, organic inhibitors tend to Water absorption (%) 0.87 0.3-2.5%
block the pores of the concrete matrix protecting the steel bars Fineness modulus 3.02 2.2-3.2
from the aggressive ions [17-20] . A certain threshold concentration
of the inhibitor always needs to be present at the steel surface Table 3: Physical properties of coarse aggregates
to assure effective inhibition [21] . Most of the previous studies PROPERTIES 10 mm 20 mm PERMISSIBLE
on the use of generic admixed inhibitors have used initial VALUES
concentration of 1% wt. of cement [22-23] . So, in the present study, Specific gravity 2.84 2.82 2.5 to 3.0
same concentration was adopted.
Water absorption (%) 0.65 0.53 Shall not be >2%
In the present study, two inhibitors on the basis of their Fineness modulus 6.24 6.95 3.3-8
functional groups (organic and inorganic) were selected to find
their efficiency in Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) concrete environment. For this purpose, two CI on the basis of their
subjected to combined chloride and carbonated environment. functional group i.e., 4-Aminobenzoic acid (AB) consisting amine
The objective of this investigation was to compare the organic group (organic) and Triethylphosphate (TEP) consist phosphate
and inorganic CI in combined corrosive environment. The (inorganic) were selected. The physical properties of AB and TEP
assessmentof corrosion process was carried out via non- CI are shown in Table 4. The nomenclature assigned to various
destructive testing, such as Half Cell Potential (HCP) and Linear control and inhibitor applied specimens are given in Table 5.
Polarization Resistance (LPR) on specimens that were exposed to For mix proportion, w/c ratio of 0.44 was used and quantity of
most aggressive environment. Carbonation and chloride profiles ingredients used is shown in Table 6.
were also recorded to study the effectiveness of ACI.
2.2 Specimen preparation
2. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE
The effect of AB and TEP were studied on the four properties
2.1 Materials used in the study of resultant concrete viz. HCP, corrosion current density,
In the present study, OPC conforming to IS: 8112- 1989 (BIS,
2013) [24] was used and physical properties are presented in Table 4: Physical and Chemical properties of
Table 1. The coarse aggregate used was crushed gravel with corrosion inhibitors
nominal maximum size of 20 mm. Locally available river sand CHEMICAL NAME 4-AMINOBENZOIC TRIETHYLPHOSPHATE
conforming to grading zone II as per IS: 383 (2002) [25] was AND FORMULA ACID (C 7 H 7 NO 2 ) (C 6 H 15 O 4 P)
used as fine aggregate. The properties of fine aggregates and Molecular structure OH O P O
coarse aggregates are shown in Table 2 and Table 3. The main O O O
focus of study is to evaluate the effect of the presence of type NH 2
of functional group in reducing combined rate of corrosion. Molar Mass 137.14 g/mol 182.15 g/mol
It was observed from the literature that inorganic compounds Physical State Powder Liquid
were more effective for chloride induced corrosion; while Appearance White-Grey Colour less
for carbonation induced corrosion, organic-based corrosion
inhibitors worked more efficiently [26-30] . The presence of these Density 1.374 g/cc 1.072 g/cc
compounds still needs to be tested in combined exposure Melting Point 188 °C -56.5 °C
30 THE INDIAN CONCRETE JOURNAL | APRIL 2021