Page 4 - Open-Access-June-2020
P. 4
TECHNICAL PAPER
Behavior of engineered
Cementitious Composite
struCtural elements Preethy Mary arulanandaM,
S. B. Singh,
– a review toShiyuki kanakuBo,
MadaPPa V.r. SiVaSuBraManian*
Abstract structural applications where the issues pertaining to damage
tolerance, energy absorption and crack control are dominant .
[5]
In this article, a comprehensive review is conducted to This material is also known as Strain-hardening Cementitious
summarize the research and development on Engineered Composite (SHCC) [6, 7] and it is a type of High Performance Fiber
Cementitious Composites (ECC) over the decades emphasizing Reinforced Cementitious Composites (HPFRCC) .
[8]
on its structural behavior. Critical observations on flexural
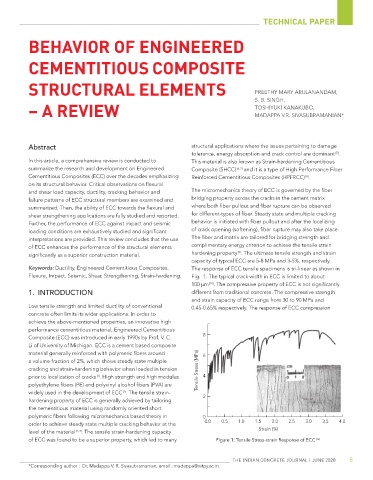
and shear load capacity, ductility, cracking behavior and The micromechanics theory of ECC is governed by the fiber
failure patterns of ECC structural members are examined and bridging property across the cracks in the cement matrix
summarized. Then, the ability of ECC towards the flexural and where both fiber pullout and fiber rupture can be observed
shear strengthening applications are fully studied and reported. for different-types of fiber. Steady state and multiple cracking
Further, the performance of ECC against impact and seismic behavior is initiated with fiber pullout and after the localizing
loading conditions are exhaustively studied and significant of crack opening (softening), fiber rupture may also take place.
interpretations are provided. This review concludes that the use The fiber and matrix are tailored for bridging strength and
of ECC enhances the performance of the structural elements complimentary energy criterion to achieve the tensile strain
[9]
significantly as a superior construction material. hardening property . The ultimate tensile strength and strain
capacity of typical ECC are 5-8 MPa and 3-5%, respectively.
Keywords: Ductility, Engineered Cementitious Composites, The response of ECC tensile specimens is tri-linear as shown in
Flexure, Impact, Seismic, Shear, Strengthening, Strain-hardening. Fig. 1. The typical crack width in ECC is limited to about
100 µm . The compressive property of ECC is not significantly
[10]
1. INTRODUCTION different from traditional concrete. The compressive strength
and strain capacity of ECC range from 30 to 90 MPa and
Low tensile strength and limited ductility of conventional 0.45-0.65% respectively. The response of ECC compression
concrete often limits its wider applications. In order to
achieve the above-mentioned properties, an innovative high
performance cementitious material, Engineered Cementitious
Composite (ECC) was introduced in early 1990s by Prof. V. C.
Li of University of Michigan. ECC is a cement based composite
material generally reinforced with polymeric fibers around
a volume fraction of 2%, which shows steady state multiple
cracking and strain-hardening behavior when loaded in tension
prior to localization of cracks . High strength and high modulus
[1]
polyethylene fibers (PE) and polyvinyl alcohol fibers (PVA) are
widely used in the development of ECC . The tensile strain-
[2]
hardening property of ECC is generally achieved by tailoring
the cementitious material using randomly oriented short
polymeric fibers following micromechanics based theory in
order to achieve steady state multiple cracking behavior at the
level of the material [3, 4] . The tensile strain-hardening capacity
of ECC was found to be a superior property, which led to many Figure 1: tensile Stress-strain response of eCC [12]
The IndIan ConCreTe Journal | June 2020 5
*Corresponding author : Dr. Madappa V. R. Sivasubramanian, email : madappa@nitpy.ac.in.