Page 18 - Open-Access-June-2020
P. 18
TECHNICAL PAPER
(a) (b)
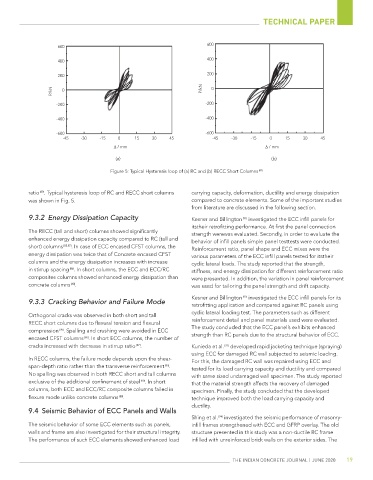
Figure 5: Typical Hysteresis loop of (a) RC and (b) RECC Short Columns [87]
ratio . Typical hysteresis loop of RC and RECC short columns carrying capacity, deformation, ductility and energy dissipation
[89]
was shown in Fig. 5. compared to concrete elements. Some of the important studies
from literature are discussed in the following section.
9.3.2 Energy Dissipation Capacity Kesner and Billington investigated the ECC infill panels for
[91]
itstheir retrofitting performance. At first the panel connection
The RECC (tall and short) columns showed significantly strength werewas evaluated. Secondly, in order to evaluate the
enhanced energy dissipation capacity compared to RC (tall and behavior of infill panels simple panel testtests were conducted.
short) columns [85,87] . In case of ECC encased CFST columns, the Reinforcement ratio, panel shape and ECC mixes were the
energy dissipation was twice that of Concrete encased CFST various parameters of the ECC infill panels tested for itstheir
columns and the energy dissipation increases with increase cyclic lateral loads. The study reported that the strength,
in stirrup spacing . In short columns, the ECC and ECC/RC stiffness, and energy dissipation for different reinforcement ratio
[86]
composites columns showed enhanced energy dissipation than were presented. In addition, the variation in panel reinforcement
concrete columns . was used for tailoring the panel strength and drift capacity.
[88]
Kesner and Billington investigated the ECC infill panels for its
[92]
9.3.3 Cracking Behavior and Failure Mode
retrofitting application and compared against RC panels using
cyclic lateral loading test. The parameters such as different
Orthogonal cracks was observed in both short and tall
RECC short columns due to flexural tension and flexural reinforcement detail and panel materials used were evaluated.
compression . Spalling and crushing were avoided in ECC The study concluded that the ECC panel’s exhibits enhanced
[90]
encased CFST columns . In short ECC columns, the number of strength than RC panels due to the structural behavior of ECC.
[86]
cracks increased with decrease in stirrup ratio . Kunieda et al. developed rapid jacketing technique (spraying)
[87]
[93]
using ECC for damaged RC wall subjected to seismic loading.
In RECC columns, the failure mode depends upon the shear- For this, the damaged RC wall was repaired using ECC and
span-depth ratio rather than the transverse reinforcement . tested for its load carrying capacity and ductility and compared
[85]
No spalling was observed in both RECC short and tall columns with same sized undamaged wall specimen. The study reported
exclusive of the additional confinement of steel . In short that the material strength affects the recovery of damaged
[90]
columns, both ECC and ECC/RC composite columns failed in specimen. Finally, the study concluded that the developed
flexure mode unlike concrete columns . technique improved both the load carrying capacity and
[88]
ductility.
9.4 Seismic Behavior of ECC Panels and Walls
Shing et al. investigated the seismic performance of masonry-
[94]
The seismic behavior of some ECC elements such as panels, infill frames strengthened with ECC and GFRP overlay. The old
walls and frame are also investigated for their structural integrity. structure presented in this study was a non-ductile RC frame
The performance of such ECC elements showed enhanced load infilled with unreinforced brick walls on the exterior sides. The
The IndIan ConCreTe Journal | June 2020 19